QUICK GUIDE TO DIAMONDS
Buying diamond jewellery is not something we do on a regular basis. So how can we know where to start?
Our guides on the finer points of diamonds are designed to help you through the maze.

Whether you are considering buying an earth or lab created diamond ring or item of diamond jewellery, our quick guide is here to help you.*
* This quick guide is specific to round brilliant cut diamonds
If you take away only one thing it should be that each diamond is very much the sum of it's parts...
WHAT MAKES ONE DIAMOND SPARKLE MORE THAN ANOTHER?
Several factors contribute to make one diamond sparkle and shimmer more than another.
The table and depth ratios of the diamond are key. This is because they inherently dictate the angles of the crown and the pavilion (and vice versa!).
What does that mean? These ratios and angles determine how light entering the surface (or 'face-up' aspect) of the diamond behaves.
The first image above shows a well proportioned table and depth with corresponding optimal crown and pavilion angles. When light enters the top of the diamond it hits the pavilion at the ideal angle to reflect across the diamond and back up again creating a visual sparkle.
However, a diamond with either proportionately excessive or shallow depth (as shown in the second and third images above) allows the light to bounce out of the diamond below the surface such that it cannot be seen.
WHAT MAKES A DIAMOND A CUT ABOVE THE REST?
There is no getting away from it. The quality of the cut of any diamond significantly determines its' scintillation and brilliance.
Nowadays, the precision with which a diamond can be cut is far superior than in years gone by.
The symmetry and fineness of the cut is key to all shapes and sizes of diamond. In the case of round brilliant cut diamonds, it is of even greater importance.
Where the cut and symmetry of a round diamond is absolutely optimal it may be referred to as ideal cut or "hearts and arrows" (although this is not a characteristic identified within a GIA grading report).
When magnified from above with a special tool, a series of eight perfectly formed arrows emanating from the table centre can be seen.
From below, a series of eight hearts are displayed around the inside of it's circumference.
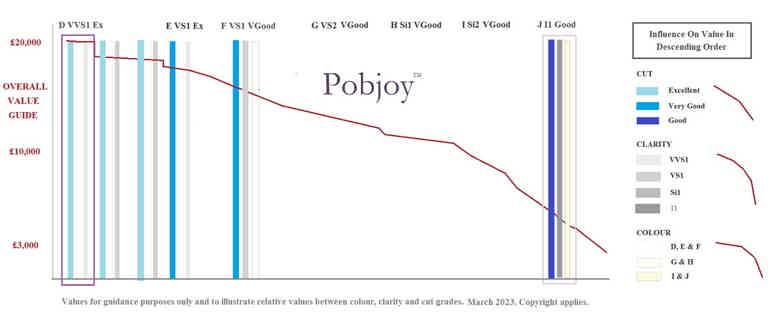
BUT I THOUGHT IT WAS ALL ABOUT COLOUR AND CLARITY?
Colour and clarity are important - it's just that they not are the only things that matter. As a rule of thumb the higher the colour and clarity grade the higher the value of the diamond.
The colour of a diamond in simplified terms refers to it's "whiteness" with "D" being at the top of the table. While a "D" colour- graded diamond is highly desirable it is not until the colour grade reaches "H" that the naked eye will notice a material change in the colour quality. This is why we tend to steer our customers towards diamonds graded E, F or G.
Clarity is concerned with how clear the diamond is specifically the amount, size and nature of blemishes, fissures and marks it contains.
An internally flawless diamond is graded "IF" which means that it contains absolutely no marks or blemishes which is extremely rare and commensurately expensive. VVS1 means Very Very Slightly Included (marked) and Si Slightly Included.
Because inclusions in diamonds are extremely difficult to see by the naked eye until grade Si2 and below on the grading table, we generally recommend opting for a diamond clarity grade of between VS1 (Very Slightly Included) and Si1. You can see the full diamond clarity table in our "4C's" section.
WATCH OUT FOR "BGM"
BGM stands for Brown, Green, and Milky. It means that sometimes a diamond can have a brown-green undertone or a milky opaqueness.
This detracts from the diamond's appearance and reduces it's value.
BGM is not something included within a diamond grading report.
All Pobjoy diamonds are screened and filtered to avoid BGM.
EYECLEAN DIAMONDS
An eyeclean diamond is one which displays no inclusions visible to the naked eye. Typically a diamond of Si1 clarity or above may be eyeclean and of sufficient colour quality, but this is not necessarily the case.
All other variables being equal, an eyeclean diamond of Si1 clarity will appear clearer to the naked eye and may be more valuable than a non-eyeclean, higher clarity grade VS2.
ABOUT THE CULET
The culet refers to the tapered lower point of a round cut diamond and is expressed as a percentage of the diamond's width.
A diamond with a larger culet is less desirable especially if it can be noticed when looking down at the face-up side of the diamond and thereby reduces it's value.
INDEPENDENT CERTIFIED GRADING
Reliable certification of diamonds is provided by credible independent gemological institutes.
These include the Gemological Institure of America (GIA), International Gemological Institure (IGI), World Gemological Institute (WGI), European Gemological Laboratory (EGL) and - for smaller melee diamonds - Hatton Garden Diamond Laboratory (HGDL)
Each of these institutes (or "laboratories") independently establish the colour, clarity, cut and carat weight of each diamond it is instructed to grade.
In turn, each institute produces a grading certificate with a unique reference number specific to each diamond it has graded.
Buying a diamond, whether earth mined or lab created, without an original certificate from a recognised and respected grading institute is to be avoided.
A certificate provided by a jeweller in it's own name or by an unrecognised grading laboratory should also be given a wide berth. This is due to the inherent conflict of interests that exist.
After all, if the diamond is what it is claimed to be, you need to ask yourself why it hasn't been graded independently and by a reputable source?
More detailed guides...
One Carat Round Brilliant Cut Diamond Value Guide
GIA Graded